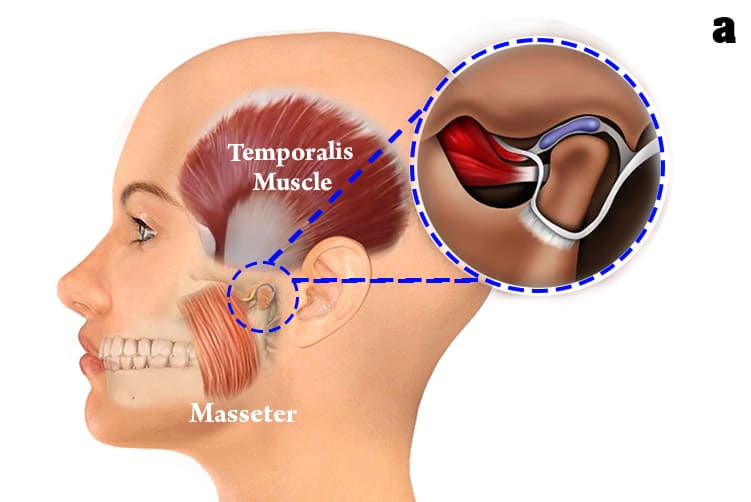
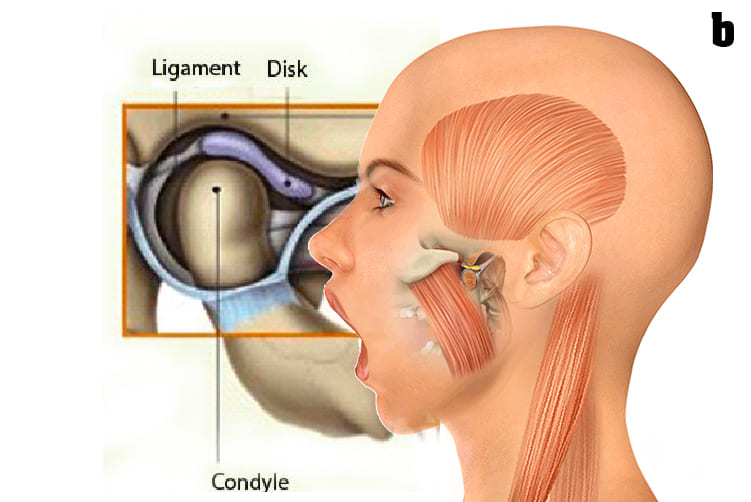
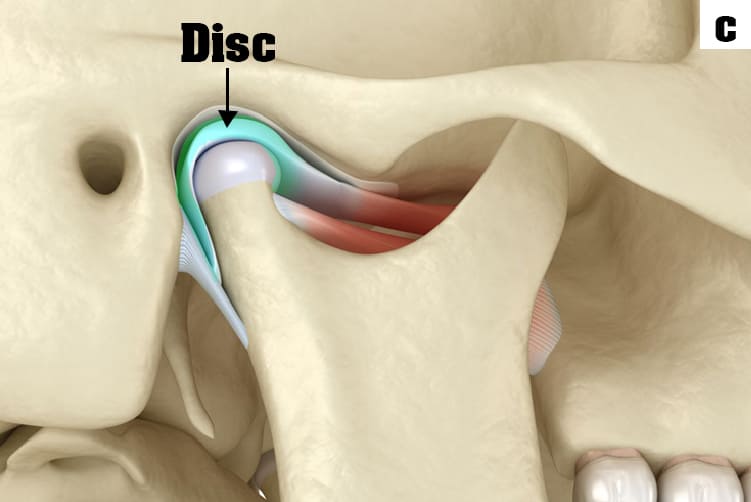
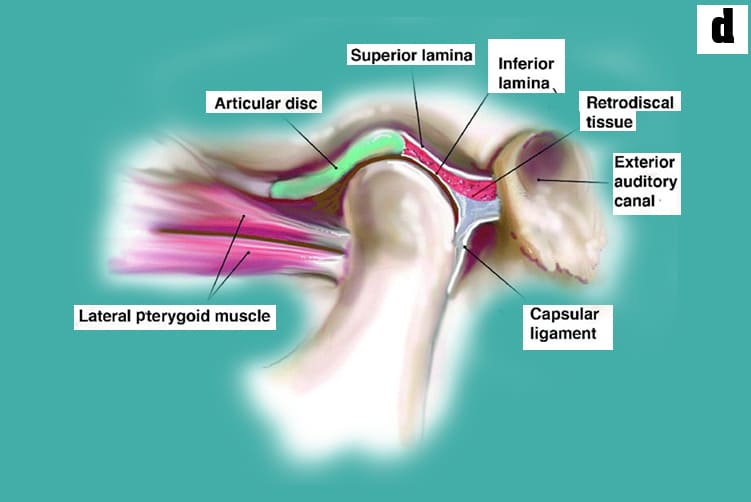
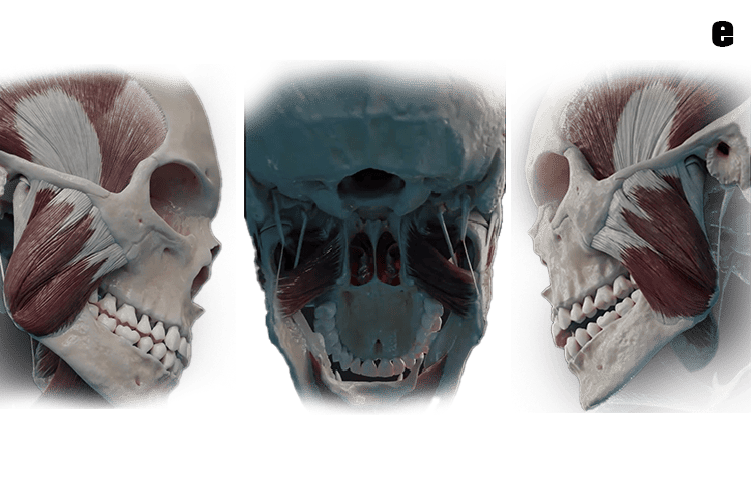
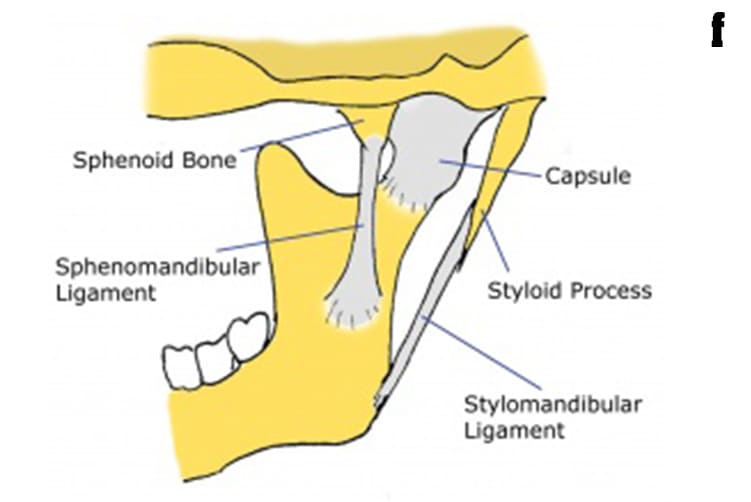
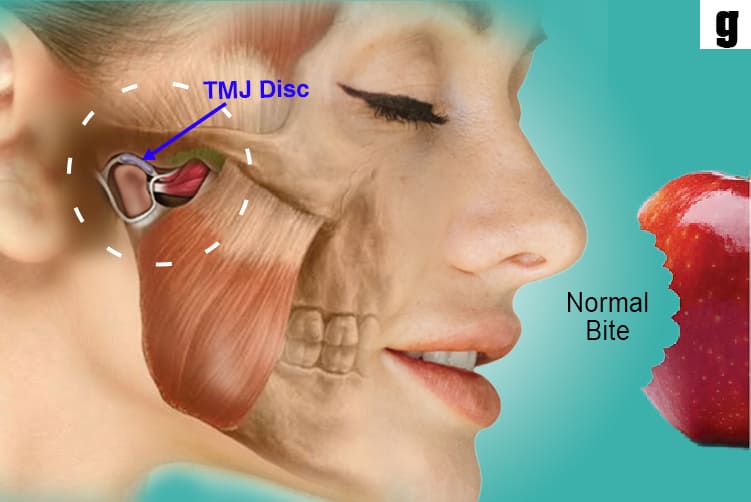
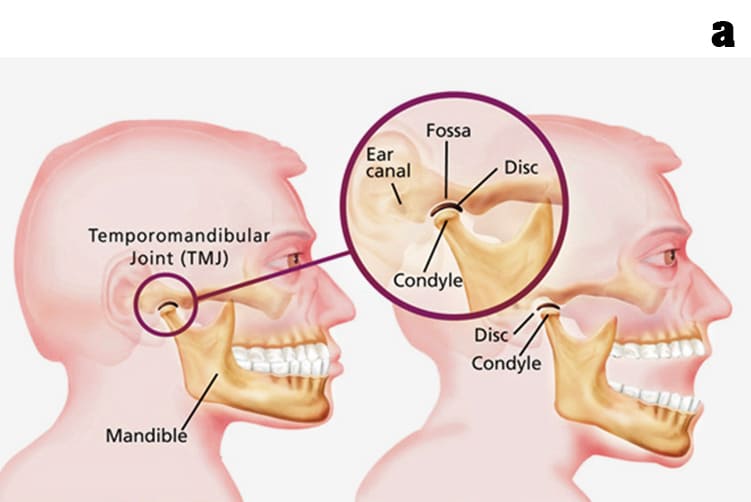
What is Temporomandibular Joints (TMJ)?
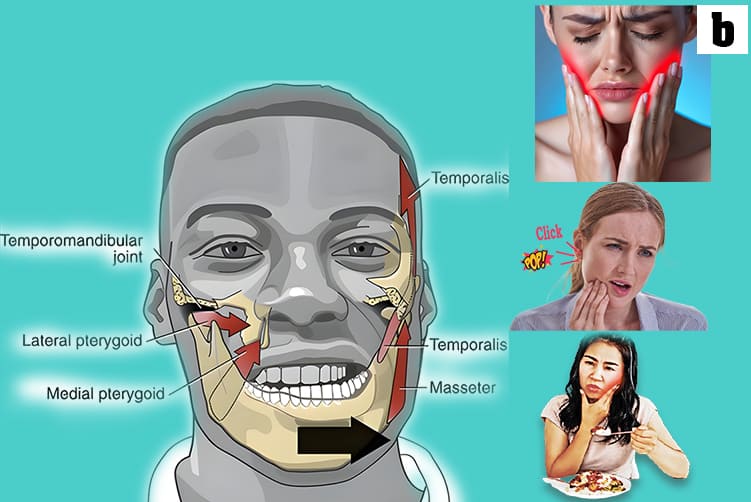
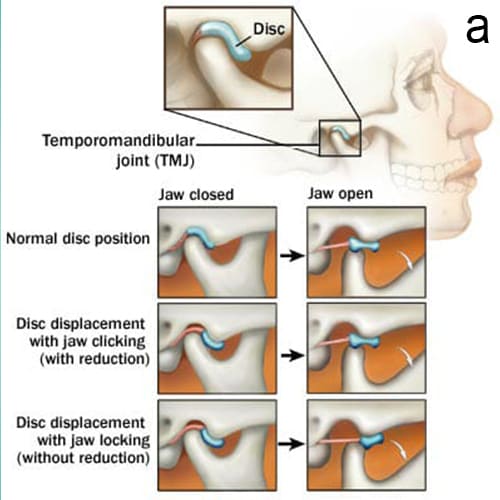
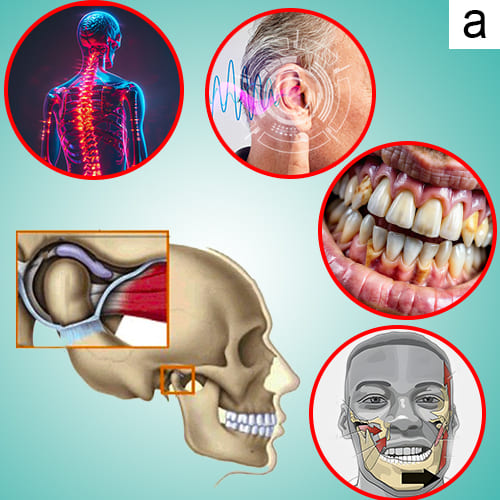
a. The TMJ is a sliding "ball and socket" Joint located in front of each ear , where the upper & lower jaws meet. Its the joint that works when the mouth is opened and closed together.
b. The ball-shaped condyle on the lower jaw glides along the socket in the skull base when you open your mouth, and slides back when you close your mouth.
c. Inside the TM joint is a disc that provides a cushion between the upper and lower jaw when it is opened and closed.
d. Connective tissue (Retrodiscal tissue) containing blood vessels and nerves attach the disc to the joint.
e. Muscles attached to the jawbone control movement and position. and work together to open and close the mouth.
f. Ligaments hold and stabilize the joint.
g. Bite is usually stable when the muscles and joints properly work together.
What is Temporomandibular Disorder(TMD)?
a. Temporomandibular disorder (TMD) refers to a group of conditions affecting the temporomandibular joints (TMJs), which connect the lower jaw to the skull.
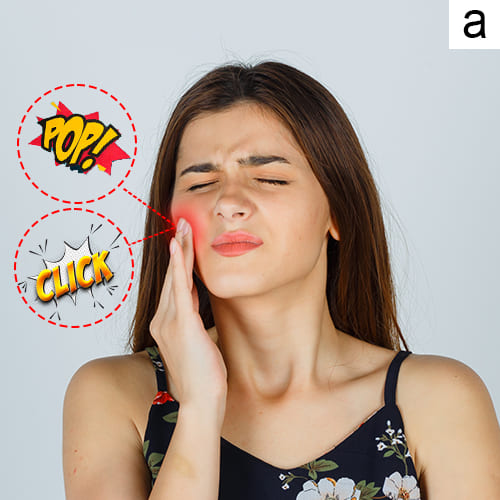
b. TMD can cause pain and dysfunction in the jaw joint and the surrounding muscles, leading to symptoms such as jaw pain, clicking sounds, and difficulty chewing.
c. The exact causes of TMD are often thought to be unclear but may include jaw injuries, muscle spasm, arthritis, teeth grinding and stress.
Why is it important to address TMD?
a. Addressing temporomandibular disorder (TMD) is important to prevent the progression of symptoms, which can lead to chronic pain and dysfunction in jaw movement.
b. Early intervention can improve quality of life by reduce pain, enhancing oral function and preventing potential damage to teeth and gums.
c. Additionally, timely treatment can reduce the need for more invasive procedures and associated Healthcare Costs in the future.
How is TMD diagnosed?
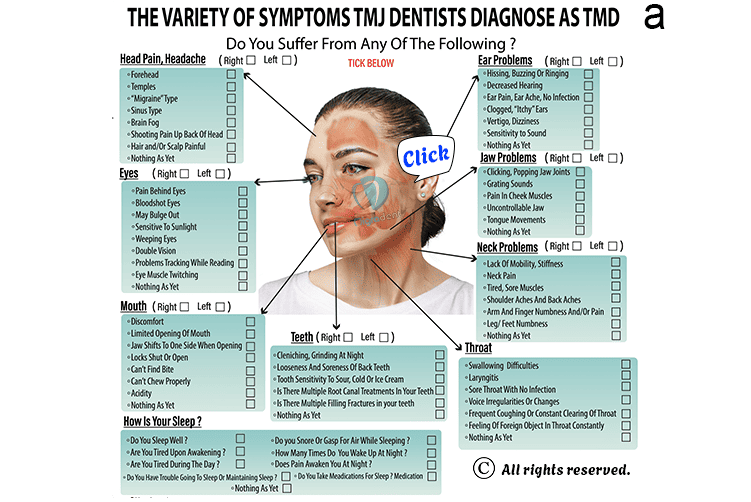
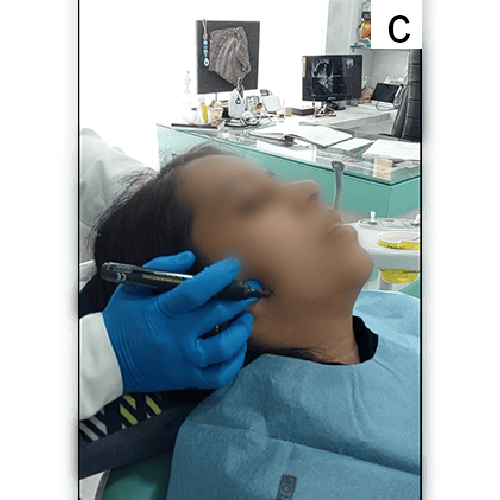
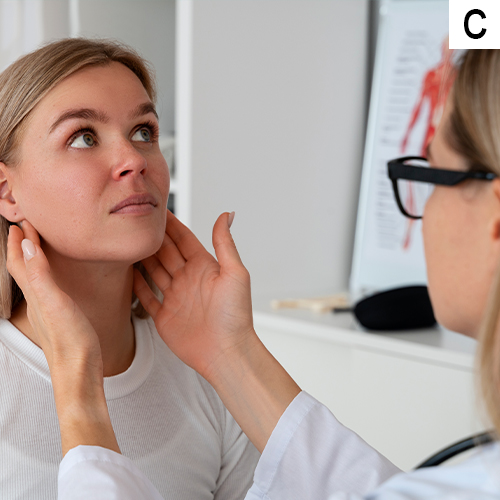
a. Temporomandibular disorder (TMD) is diagnosed primarily through a detailed medical history and physical examination, focusing on symptoms such as jaw pain and clicking sounds.
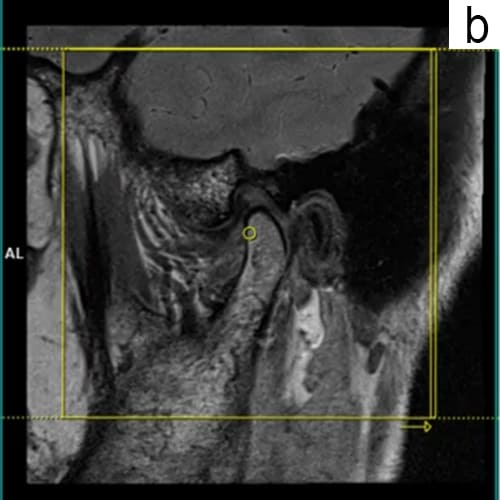
b. Clinicians may use the Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (DC/TMD), which includes both clinical assessments and imaging techniques like MRI or X-rays to evaluate joint function and rule out other conditions.
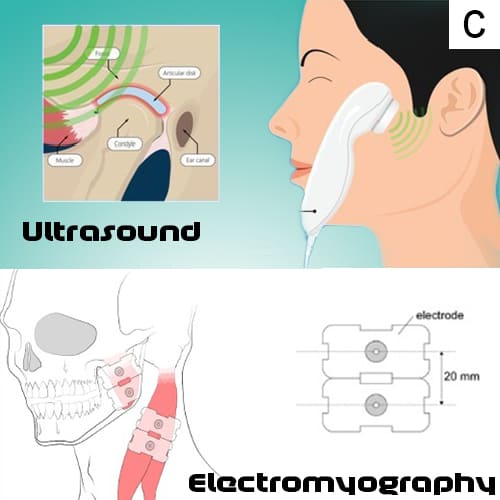
c. Additional diagnostic tools may include ultrasound and electromyography to assess muscle function and joint health.
When should I seek evaluation for TMD?
a. You should seek evaluation for Temporomandibular Disorder (TMD) if you experience persistent jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds during jaw movement or difficulty opening and closing your mouth.
b. Additionally, if you have headaches, earaches or facial pain that may be related to jaw function, it's important to consult a TMD specialist.
c. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and improve overall quality of life.
a)If temporomandibular disorder (TMD) is not Treated, it can lead to chronic pain, dental issues, and potential hearing problems due to joint dysfunction.
b)Additionally, untreated TMD may result in significant impacts on quality of life, including mental health challenges and difficulty performing daily activities.
Myth:only surgery can treat TMD!
a. The myth that only surgery can treat temporomandibular disorder (TMD) is misleading, as many patients benefit from conservative, non-invasive treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and self-management strategies.
b. Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases where conservative methods have failed, highlighting the importance of .
Myth: TMD is a rare condition!
a. The myth that Temporomandibular disorder (TMD) is a rare condition is inaccurate, as studies indicate that it affects a significant portion of the population. Research shows that approximately 31% of adults and 11% of children experience TMD symptoms, with prevalence rates varying between 5% to 40% in different populations.
b. This widespread occurrence highlights the importance of awareness and appropriate management of TMD.
Why Choose Migradent for Temporomandibular disorders (TMD)?
Dr. Sarrah Husain at MIGRADENT brings extensive experience and expertise in orofacial pain management. With a patient-centered approach, she aims to accurately diagnose the underlying cause of orofacial pain and develop personalized treatment plans for effective pain relief, improved oral health, and enhanced overall well-being.